Cannabis, a plant that has captivated the interest of many, is more than just a source for psychoactive and medicinal compounds. Understanding the anatomy of the reproductive organs in the cannabis plant is crucial for both cultivators and cannabis consumers. This article delves deep into the world of cannabis plants, unraveling their complex structure and the unique characteristics that differentiate male and female plants. By exploring the depths of cannabis plant anatomy, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide that enlightens and educates.
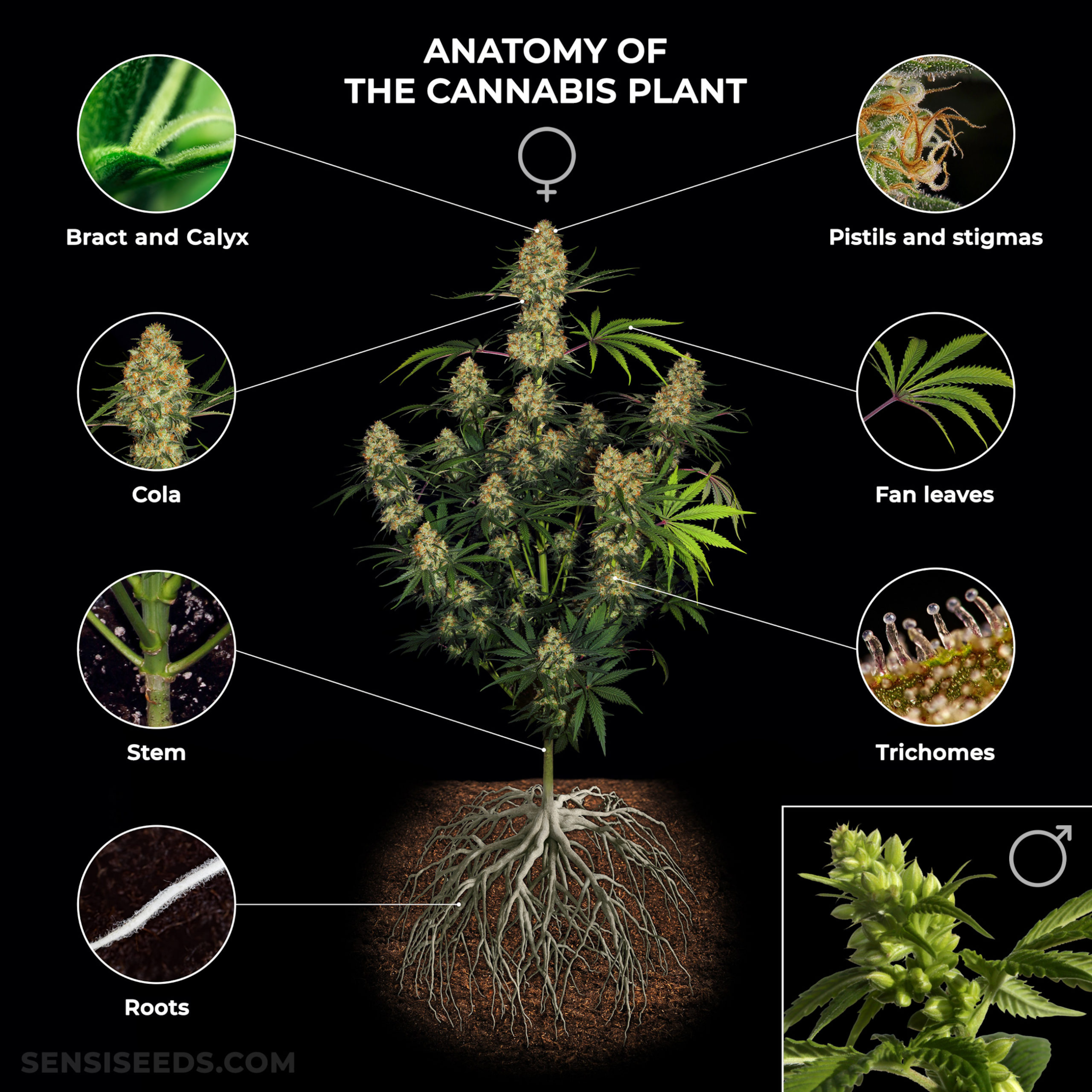
Overview of Cannabis Plants
Cannabis plants are part of a group known as dioecious plants, meaning they exist as separate male and female plants. This distinction in the dioecious plant world is particularly significant as it plays a crucial role in the reproduction and cultivation processes of cannabis. Understanding the differences between male and female cannabis plants is vital for growers, especially those looking to produce seeds or cultivate high-quality cannabis flowers.
The General Anatomy of Cannabis Plants
At the heart of understanding cannabis plant anatomy lies the recognition of its key structural components. The cannabis plant consists of several parts, each playing a pivotal role in its growth and development.

The Main Stem
The main stem, or the central support structure, is crucial for the overall stability and growth of the cannabis plant. It not only supports the plant’s structure but also acts as a conduit, transporting vital nutrients and water from the roots to the rest of the plant. The robustness of the main stem often indicates the overall health and vigor of the cannabis plant.
Root System
Beneath the surface, the cannabis root system forms the foundation of the plant’s health and growth. Roots not only anchor the plant in the soil but also absorb water and essential nutrients required by weed plant for growth. A healthy root system is a key indicator of a thriving cannabis plant, and understanding its development is essential for successful cannabis cultivation.
Leaf Growth and Plant Structure
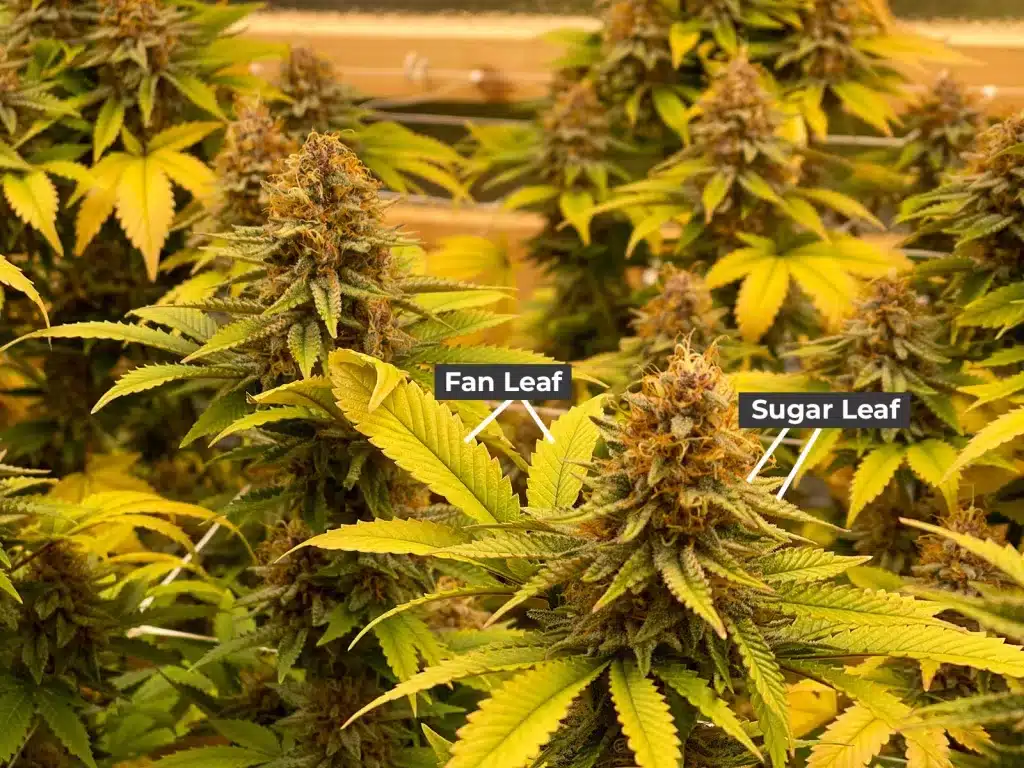
Leaves are one of the most recognizable features of cannabis plants. They are primarily responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light into the energy needed for growth. Cannabis plants exhibit a variety of leaf patterns and structures, with fan leaves and sugar leaves being the most prominent types. Fan leaves, with their iconic shape, are larger and responsible for capturing sunlight, while sugar leaves, smaller and more abundant near the flowers, are covered with resin glands that produce cannabinoids and terpenes.

Differentiating Male and Female Cannabis Plants
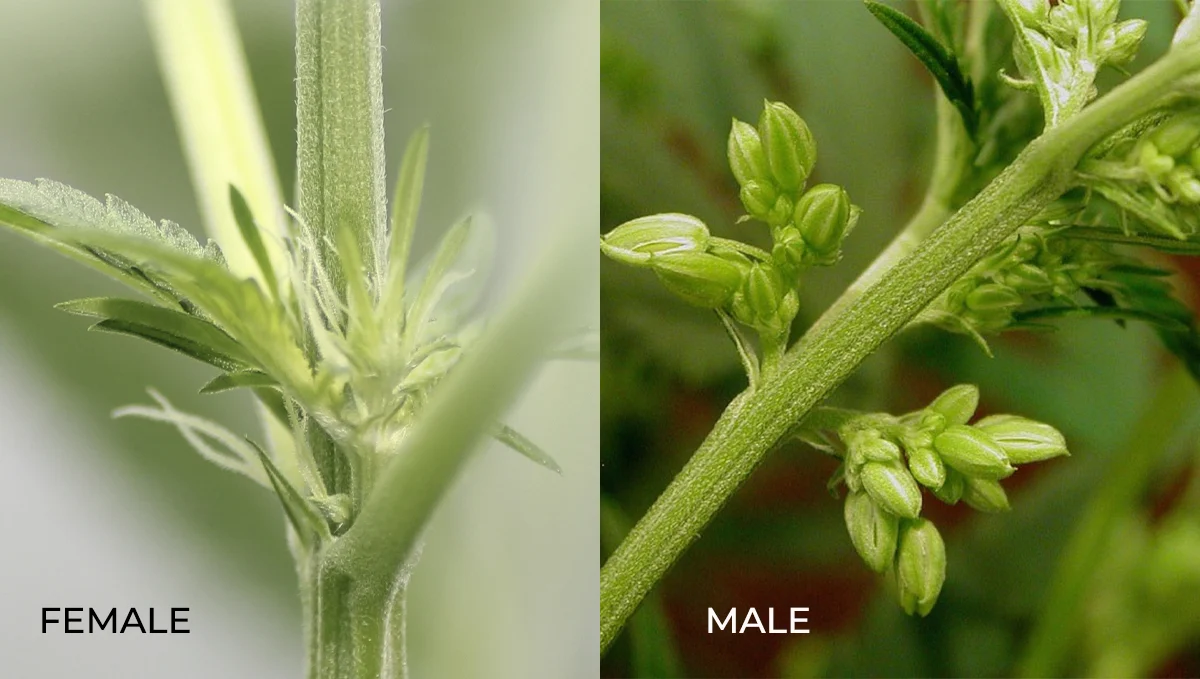
The ability to distinguish between male and female cannabis plants is a skill of paramount importance for growers. Male cannabis plants are known for their pollen sacs, which release pollen to fertilize female plants. Female cannabis plants start, on the other hand, produce the coveted cannabis flowers or buds when unfertilized. Recognizing the pre-flowers, which appear at the nodes of the plant, is crucial in identifying the plant’s sex early in the growth cycle. Male pre-flowers are small and round, while female pre-flowers are more elongated and feature tiny hair-like structures known as stigmas.
In this first section, we have laid the foundation for understanding the complex world of cannabis plant anatomy. As we delve further into the details of each component, from roots to flowers, we will uncover the intricacies that make the cannabis plant a fascinating subject for study and cultivation.
Detailed Anatomy of the Cannabis Plant
Delving deeper into the anatomy of the cannabis plant, we uncover the intricate details that define its unique characteristics. Each component, from roots to flowers, plays a pivotal role in the marijuana plant’s life cycle and overall health.
Exploring Main Components
Cannabis Roots
The roots of a cannabis plant, often hidden beneath the soil, are vital for its survival. They serve two primary functions: anchoring the plant securely in the ground and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. The health of a cannabis plant is largely dependent on the health of its roots. A strong root system contributes to the robust growth of the entire plant.
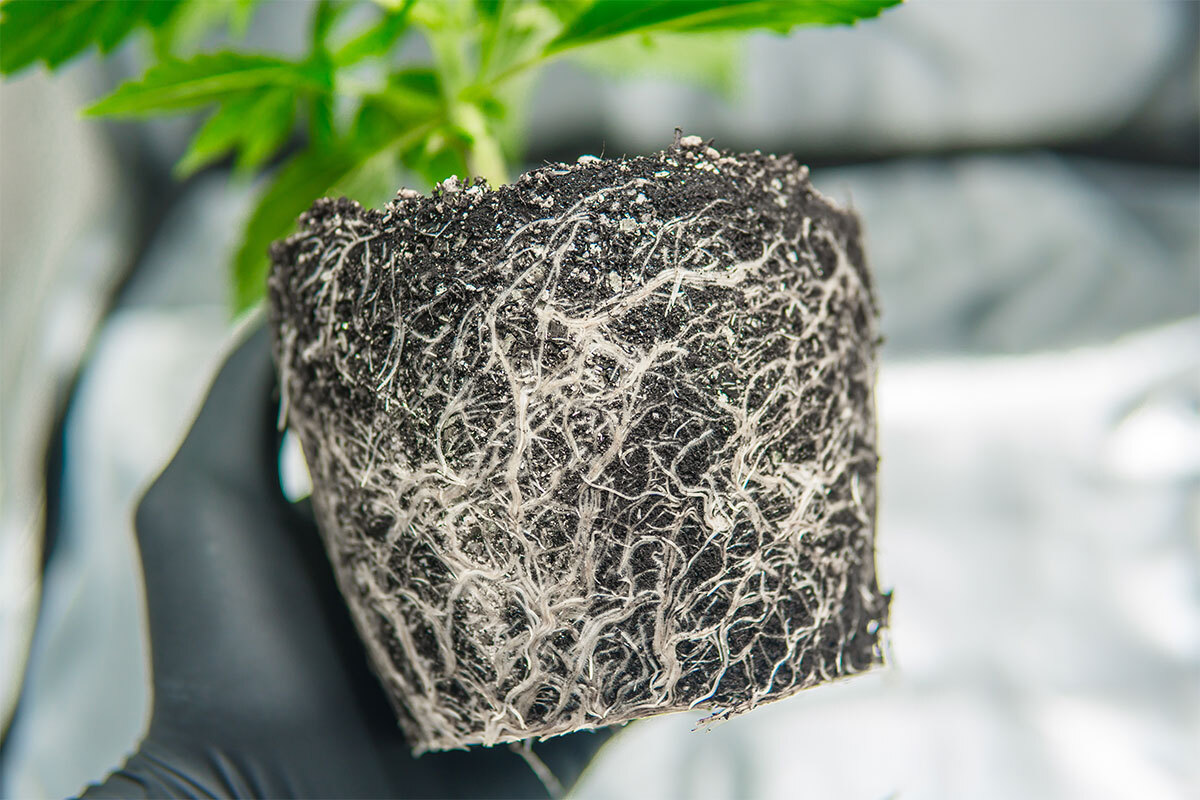

Stem and Leaf Structure
The stem of a cannabis plant grows and functions as the main support and transport system. It ensures that nutrients and water travel from the roots to the leaves and flowers. Leaves, particularly fan leaves and sugar leaves, are essential for photosynthesis. Fan leaves, with their broad surface area, capture sunlight and produce energy, while sugar leaves, smaller and located closer to the flowers, are covered in resin glands.
Indica vs. Sativa Leaves
Cannabis leaves vary depending on the plant species. Indica leaves are typically broader and darker in color, while sativa leaves are narrower and lighter. This distinction is not just aesthetic but also indicative of the plant’s genetic makeup and growth patterns.
The Role of the Vascular System
The vascular system in cannabis is responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant. This system, comprising xylem and phloem, is crucial for the plant’s growth and ability to respond to environmental conditions.
The Cannabis Flower: A Closer Look
The flowers of cannabis plants, especially in female plants, are of significant interest due to their high concentration of cannabinoids and terpenes.
Anatomy of Female Cannabis Plant
The female cannabis plant is distinguished by its ability to produce flowers or buds. These buds collect pollen are the primary source of cannabinoids like THC and CBD. The flower structure is complex, with several key components like the calyx, trichomes, and pistils. The pistils contain the stigmas, which catch pollen from male plants for fertilization.
Male Cannabis Plants and Pollen Sacs
Male marijuana plant plants play a crucial role in the reproduction cycle. They develop pollen sacs, which release pollen to fertilize female marijuana plant plants. While male plants are typically less desired in the cultivation of high-THC buds, they are essential for breeding and seed production.

The Flowering Stage
The flowering stage in cannabis plants is a critical phase in the plant’s life cycle. This is when female plants develop buds, and male plants produce pollen. Understanding the flowering stage is crucial for growers, as it determines the timing of important cultivation practices like pruning and harvesting.
Pollen Sacs and Reproduction
Pollen sacs, found on male cannabis plants, play a crucial role in the reproductive process. These sacs burst open to release pollen, which can be carried by wind or direct contact to female plants. The fertilization process involves the transfer of pollen to the female plant’s ovule, leading to seed production.
Cannabis Flower Development
In female cannabis plants, the flowers develop at the nodes, where the branches meet the stem. These flowers are initially small, but they grow and develop a complex structure as the plant matures. The flowering stage is influenced by several factors, including light exposure, temperature, and the plant’s genetic makeup.
Significance of Trichomes
One of the most distinctive features of cannabis flowers is the presence of trichomes. These tiny, crystal-like structures cover the surface of the buds and leaves surrounding the flower. Trichomes are responsible for producing and storing cannabinoids and terpenes, the compounds that give cannabis its unique properties and aroma.

Resin Gland Production
Trichomes are essentially resin glands. They produce a sticky resin that contains high concentrations of cannabinoids and terpenes. This resin serves several purposes, including protecting the plant from pests and environmental stressors. It’s also the part of the plant most valued for its therapeutic and psychoactive effects.
In these sections, we have explored the detailed anatomy of the cannabis plant, focusing on its roots, stem, leaves, and flowers. We have also discussed the critical role of the vascular system and the distinctive features of the cannabis flower, including trichomes and resin glands. Understanding these components is essential for anyone interested in cannabis cultivation or consumption, as it provides insight into the plant’s growth, health, and the quality of its yield.
Cannabis Seeds and Propagation
The journey of a cannabis plant begins with a seed, an encapsulation of potential waiting to unfold. Understanding the intricacies of cannabis seeds and the methods of propagation is essential for successful cultivation.

Understanding Cannabis Seeds
Cannabis seeds are the starting point of the life cycle of a cannabis plant. These seeds contain the genetic blueprint of the plant, determining traits such as size, potency, and resilience. Seeds can be either feminized, ensuring they grow into female plants, or regular, where the outcome of male or female plants is uncertain. The germination of cannabis seeds is the first step in the cultivation process, leading to the seedling stage where the initial growth of the plant begins.
Seed Production
The process of seed production in cannabis involves the fertilization of a female plant by a male plant. Male plants produce pollen, which fertilizes the female plant’s ovules, leading to seed production. These seeds can be harvested and used for growing new cannabis plants. Seed production is a critical aspect of cannabis cultivation, especially for breeders looking to develop new strains or preserve existing ones.
Methods of Propagation
Cannabis can be propagated in several ways. The most common method is through seeds, but another effective method is cloning. Cloning involves taking a cutting from a mature plant and allowing it to root and grow as an independent plant. This method ensures that the new plant will have the same genetic makeup as its parent, which is particularly valuable for maintaining the consistency of a strain.
The Unique Aspects of Cannabis Plant Anatomy
The cannabis plant is endowed with several unique features that set it apart from other plant species. These features not only contribute to the plant’s distinctive appearance but also play a role in its cultivation and the quality of its produce.
Sugar Leaves and Their Uses
Sugar leaves are small leaves that are found in and around the cannabis flower. They get their name from the sugary appearance caused by the trichomes covering them. While not as prominent as the larger fan leaves, sugar leaves are significant because they are rich in trichomes, making them a valuable source of cannabinoids and terpenes. They are often used in the production of cannabis concentrates and edibles.
Fan Leaves vs. Sugar Leaves
The distinction between fan leaves and sugar leaves is important in cannabis cultivation. Fan leaves are the large, iconic leaves that are most often associated with the cannabis plant. They play a crucial role in photosynthesis, absorbing sunlight to produce energy for the plant. Sugar leaves, on the other hand, are smaller and more abundant in trichomes. While fan leaves are typically removed during the trimming process, sugar leaves are
often kept due to their high resin content, especially when the plant is being harvested for cannabis concentrates.

Resin Glands and Tiny Crystals
The resin glands of a cannabis plant, predominantly found in the trichomes, are responsible for the production of the tiny crystals that cover the buds and leaves. These crystals are a treasure trove of cannabinoids and terpenes, the compounds responsible for the plant’s psychoactive and therapeutic effects. The density and quality of these trichomes play a crucial role in determining the potency and flavor profile of the cannabis.
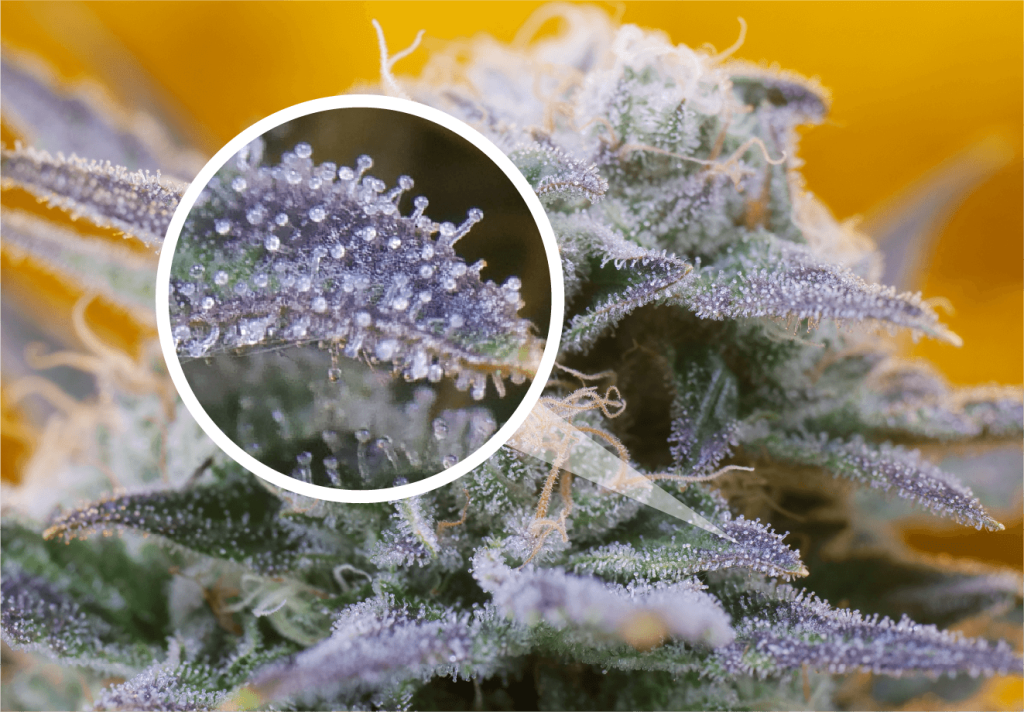

Mushroom-Shaped Glands
The trichomes on a cannabis plant, particularly those on the flowers and sugar leaves, often take on a mushroom-like shape. These glandular structures are not just a fascinating aspect of plant anatomy; they are the main factories for cannabinoid and terpene synthesis. The shape and size of these trichomes can vary based on the strain and growing conditions, influencing the plant’s resin production and, ultimately, its quality.
In these sections, we delved into the world of cannabis seeds and propagation, highlighting the importance of understanding seed production and the various methods of growing cannabis. We also explored the unique aspects of the cannabis plant anatomy, such as sugar leaves, fan leaves, resin glands, and the distinctive mushroom-shaped trichomes. These elements are not only vital for the plant’s survival and reproduction but also greatly influence the quality and properties of the cannabis produced. As we continue to explore the cannabis plant’s anatomy, we gain a deeper appreciation for its complexity and the myriad factors that contribute to its growth and potency.
Growth and Development of Cannabis Plants
The growth and development of cannabis plants are fascinating processes, marked by distinct stages and influenced by various environmental factors. Understanding these stages and factors is crucial for effective cultivation.
Life Cycle of the Cannabis Plant
The life cycle of a cannabis plant is broadly divided into four stages: germination, seedling, vegetative, and flowering. Each stage has its unique requirements in terms of light, water, and nutrients. The germination stage involves sprouting from a seed. The seedling stage is characterized by the development of cotyledon leaves, followed by the appearance of the first true cannabis leaves. During the vegetative stage, the plant undergoes significant growth in size and leaf development. Finally, in the flowering stage, female plants develop buds, while male plants produce pollen.
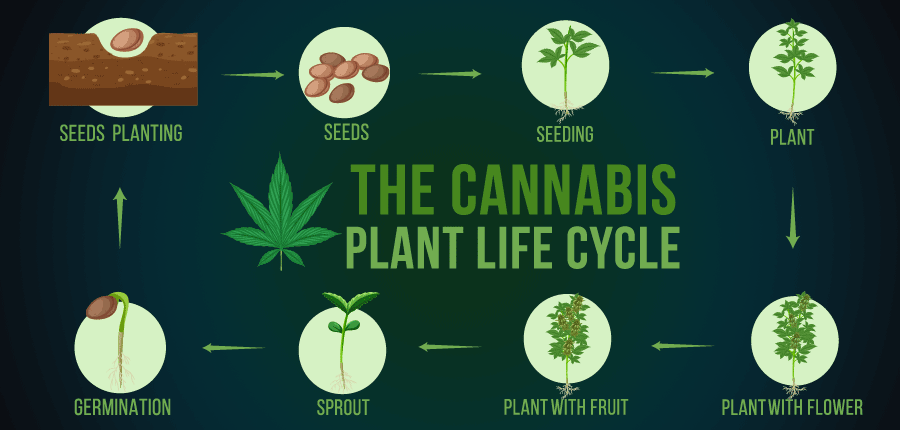
The Growth Process
Cannabis plants undergo a remarkable transformation during their growth. In the early stages, focus is on developing a strong root system and a sturdy stem, setting the foundation for later growth. As the plant matures, leaf growth appears, with new leaves and branches developing rapidly. The transition to the flowering stage is triggered by changes in the light cycle, with plants requiring longer periods of darkness to start flowering.
Environmental Factors Affecting Growth
Several environmental factors play a crucial role in the growth and development of cannabis plants. These include light, temperature, humidity, and soil quality. Cannabis plants require an optimal balance of these factors to thrive. For instance, too much or too little light can affect the growth rate and health of the plant. Similarly, temperature and humidity levels must be carefully controlled to prevent issues like mold growth or heat stress.
Practical Aspects of Cannabis Plant Anatomy for Growers
For those involved in the cultivation of cannabis, understanding the plant’s anatomy is not just academic; it has practical implications for the yield and quality of the crop.
Identifying the Sex of Cannabis Plants
One of the most critical skills for a cannabis grower is the ability to identify the sex of the plants early in the growth cycle. This is crucial because male plants, while essential for breeding, are often removed from the grow space to prevent the fertilization of female plants, which can result in a lower yield of consumable buds.
Maximizing Yield
Knowledge of cannabis plant anatomy aids growers in maximizing their yield. Practices such as pruning, training, and ensuring proper nutrient intake are fundamental. Understanding the main cola (the primary bud site) and how to develop more bud sites through techniques like topping and LST (Low-Stress Training) can significantly increase yield.
Maintaining Plant Health
A deep understanding of cannabis anatomy is also crucial for maintaining plant health. Recognizing signs of nutrient deficiencies, pest infestations, or diseases early can make a substantial difference in the plant’s ability to recover and flourish.
The journey through the world of cannabis plant reveals a plant with remarkable adaptability and complexity. From its diverse root systems to the intricacies of its flowers and leaves, each aspect of the cannabis plant plays a vital role in its life cycle and the qualities of the final product. For growers, this knowledge is power – the power to cultivate plants more effectively, to produce higher quality yields, and to innovate in breeding and cultivation techniques.
For enthusiasts and consumers, a deeper understanding of cannabis anatomy enriches the experience, offering insights into what makes each strain unique and how different cultivation practices impact the quality and effects of cannabis. It’s a reminder that behind every cannabis product lies a sophisticated interplay of science and nature.
As the cannabis industry continues to evolve and expand, the importance of understanding cannabis anatomy will only grow. Whether for cultivation, medical research, or simply a deeper appreciation of this versatile plant, the insights gained from studying cannabis anatomy are invaluable.








