Definition:
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex network of receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes found throughout the human body, playing a crucial role in regulating physiological processes such as mood, pain sensation, appetite, immune function, and stress response.
Purpose and Usage
The ECS is essential for maintaining homeostasis, or balance, within the body. It helps regulate and stabilize various functions, ensuring that systems like the nervous, immune, and digestive systems respond appropriately to changes. The ECS is especially relevant in the context of medical cannabis, as it interacts with cannabinoids to influence a wide range of effects.
How It Relates to Cannabis
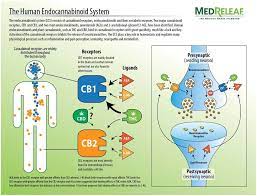
- Components of the Endocannabinoid System:
- Endocannabinoids: These are naturally occurring molecules in the body (e.g., anandamide and 2-AG) that bind to cannabinoid receptors.
- Cannabinoid Receptors: Primarily CB1 (found in the brain and central nervous system) and CB2 (found in the immune system). These receptors interact with both endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (cannabinoids from cannabis).
- Enzymes: Enzymes like FAAH and MAGL break down endocannabinoids after they have carried out their function.
- How Cannabis Interacts with the ECS:
- THC (tetrahydrocannabinol): The primary psychoactive cannabinoid in cannabis that binds to CB1 receptors, mimicking the action of endocannabinoids to produce euphoric and pain-relieving effects.
- CBD (cannabidiol): A non-psychoactive cannabinoid that interacts with CB2 receptors and can modulate the effects of THC, promoting relaxation, reducing inflammation, and providing therapeutic benefits without a “high.”
- Other Cannabinoids: Minor cannabinoids like CBG and CBN also interact with the ECS, contributing to various therapeutic effects.
- Role of the ECS in Cannabis Effects:
- The ECS helps regulate how the body responds to the cannabinoids from cannabis, influencing everything from pain relief to mood stabilization.
- By interacting with the ECS, cannabis compounds like THC and CBD can produce therapeutic effects such as pain relief, reduced anxiety, and improved sleep quality.
Common Misconceptions
- The ECS only functions when cannabis is consumed: The ECS operates continuously in the body, regulating bodily functions even without cannabis use.
- The ECS is only involved in the “high”: While THC interacts with the ECS to produce psychoactive effects, the ECS is involved in a wide variety of processes, including immune function, metabolism, and cognitive function.
- Cannabis is the only way to influence the ECS: While cannabis compounds interact with the ECS, other substances like exercise, diet, and stress management can also influence its function.
Alternatives
- Phytocannabinoids: Compounds derived from cannabis plants (e.g., THC, CBD) that directly interact with the ECS.
- Synthetic Cannabinoids: Lab-created compounds designed to mimic the effects of natural cannabinoids and interact with ECS receptors.
Importance of Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system is a cornerstone of understanding how cannabis affects the human body. It regulates a vast array of physiological processes, making it essential for maintaining overall health and balance. By interacting with the ECS, cannabis compounds provide therapeutic benefits, from pain management to anxiety relief. The study of the ECS is critical for advancing medical cannabis use and understanding the broader impacts of cannabinoids on human health.