When discussing cannabis, the conversation often revolves around cannabinoids like THC and CBD. However, terpenes, the aromatic compounds responsible for cannabis’ unique flavor profiles and therapeutic properties, play an equally important role in the overall experience. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fascinating world of terpenes, their impact on the cannabis experience, and their potential health benefits.
What are Terpenes?
Terpenes are organic compounds found in a wide variety of plants, including cannabis. They are responsible for the distinct aromas and flavors that characterize each plant species. In cannabis, terpenes contribute to the plant’s unique scent and taste, which can range from sweet and fruity to earthy and pungent. Beyond their sensory impact, terpenes also have potential therapeutic properties and are believed to work synergistically with cannabinoids to enhance their effects.
How are Terpenes Produced in Cannabis?
Terpenes are produced within the trichomes, the tiny, hair-like structures that cover the surface of cannabis flowers and leaves. Trichomes are the primary site for the biosynthesis of cannabinoids and terpenes, which occurs through a series of enzymatic reactions involving precursor molecules.
During the cannabis plant’s growth and maturation, terpene production is influenced by various factors, including genetics, environmental conditions, and cultivation techniques. By manipulating these factors, growers can optimize terpene profiles to achieve desired aromas, flavors, and potential therapeutic effects.
Common Terpenes Found in Cannabis
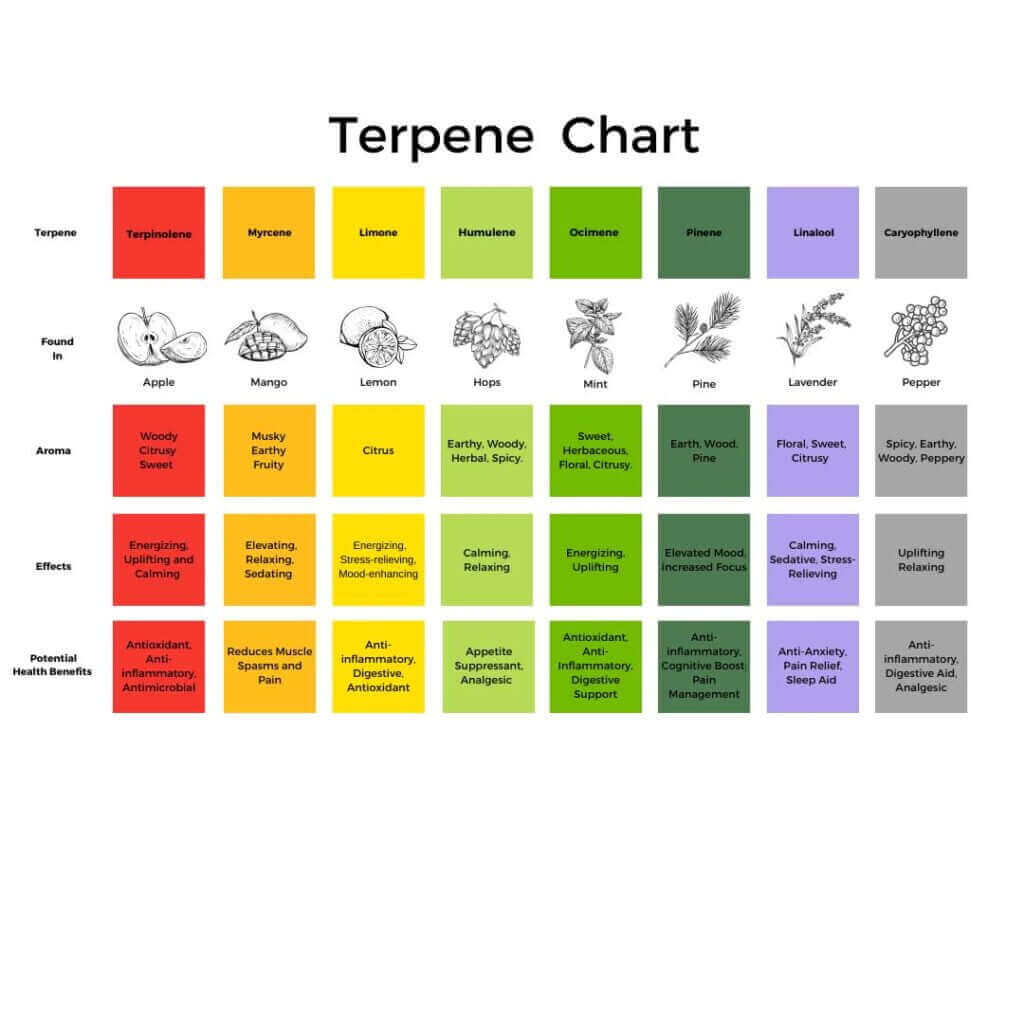
There are over 200 different terpenes identified in cannabis, each with unique characteristics and potential health benefits. Some of the most common terpenes found in cannabis strains include:
- Myrcene: The most abundant terpene in cannabis, myrcene has an earthy, musky aroma and is also found in hops, thyme, and lemongrass. Myrcene is believed to have potential anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and sedative effects.
- Limonene: Known for its citrusy aroma, limonene is found in citrus fruits, juniper, and peppermint. Limonene has potential mood-enhancing, anti-anxiety, and stress-relieving properties.
- Pinene: As the name suggests, pinene has a pine-like scent and is found in pine trees, rosemary, and basil. Pinene is believed to have potential anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator, and memory-enhancing effects.
- Linalool: With a floral, lavender-like aroma, linalool is found in lavender, coriander, and cinnamon. Linalool has potential anti-anxiety, sedative, and analgesic properties.
- Caryophyllene: Known for its spicy, peppery aroma, caryophyllene is found in black pepper, cloves, and cinnamon. Caryophyllene is unique among terpenes, as it can also act as a cannabinoid by binding to CB2 receptors, potentially providing anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
The Entourage Effect: How Terpenes Work with Cannabinoids
The entourage effect is a phenomenon in which the combined effects of cannabinoids and terpenes are greater than their individual effects. Terpenes are believed to modulate the actions of cannabinoids by interacting with the endocannabinoid system and other receptor pathways, enhancing or mitigating certain effects.
For example, myrcene may enhance the sedative effects of THC, while limonene could potentially counteract THC-induced anxiety. Understanding the entourage effect and the specific interactions between terpenes and cannabinoids can help users customize their cannabis experience and maximize potential therapeutic benefits.
Terpenes and Potential Health Benefits
Beyond their role in modulating the effects of cannabinoids, terpenes have a range of potential health benefits on their own. Many terpenes possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, which can contribute to overall health and well-being. Research into the therapeutic potential of individual terpenes is ongoing, but preliminary studies suggest that they may have a variety of applications, from pain management and stress relief to immune support and neurological health.

Terpene Extraction and Isolation
As the interest in terpenes continues to grow, so too does the demand for terpene-rich products, such as essential oils, tinctures, and concentrates. Terpene extraction involves separating the terpenes from the plant material, typically using methods like steam distillation, cold pressing, or solvent extraction. These processes result in the production of isolated terpenes, which can be used for a variety of applications, including aromatherapy, perfumery, and even food and beverage flavoring.
Customizing the Cannabis Experience with Terpenes
One of the most exciting aspects of terpenes is their potential to customize the cannabis experience to suit individual preferences and therapeutic needs. By understanding the unique properties of each terpene and how they interact with cannabinoids, users can tailor their consumption based on desired effects, flavors, and aromas.
For example, a user seeking stress relief might choose a strain rich in linalool and limonene, while someone looking for an uplifting, creative experience might opt for a strain high in pinene and terpinolene. With the growing availability of terpene-rich products and strains, the possibilities for personalizing the cannabis experience are virtually limitless.
Terpenes are the unsung heroes of the cannabis experience, playing a crucial role in shaping the plant’s unique flavor profiles, aromas, and potential therapeutic properties. By exploring the diverse world of terpenes and their synergistic relationship with cannabinoids, users can better appreciate the intricacies of cannabis and unlock its full potential. As research into the therapeutic applications of terpenes continues to expand, we can expect to see even greater interest in these remarkable compounds and the myriad ways they can enhance the cannabis experience.