Marijuana, also known as weed, cannabis, or pot, is one of the most widely used substances in the world. Whether for recreational or medicinal use, many users eventually ask: How long does weed stay in your system? The answer depends on multiple factors, including frequency of use, body composition, and the type of drug test being administered.
Unlike alcohol, which clears quickly, THC is fat-soluble, meaning it can linger in the body for weeks. The exact detection time depends on multiple factors such as frequency of use, body fat, and metabolism.
With drug testing still a common practice in workplaces, sports, and legal settings, understanding THC metabolism, detection windows, and influencing factors is crucial. Unlike substances like alcohol, which the body rapidly processes, THC lingers in fat cells, meaning detection times can range from a few days to over a month, depending on individual factors.
How the Body Processes THC
What Happens When You Consume Cannabis?
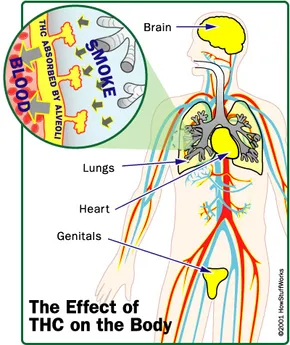
The effects of cannabis come from delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in marijuana. Once consumed, THC quickly enters the bloodstream and travels to the brain, where it binds to cannabinoid receptors and produces effects such as euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, and increased appetite.
However, even after the effects wear off, THC remains in the body as metabolites, which can be detected for extended periods.
THC Metabolism and Breakdown
After cannabis is ingested, the liver breaks down THC into metabolites, primarily:
- 11-OH-THC (11-hydroxy-THC): A psychoactive metabolite that contributes to the high.
- THC-COOH (11-nor-9-carboxy-THC): A non-psychoactive metabolite stored in fat cells and slowly excreted through urine and feces.
Since THC is fat-soluble, it is stored in fat cells rather than being water-soluble like alcohol. This means it leaves the body at a slower rate, especially for chronic users who accumulate higher levels over time.
How Long Does THC Stay in Your Body?
The duration that THC stays in your body varies depending on usage patterns, metabolism, and the test used. Below is a general guide for different test types:
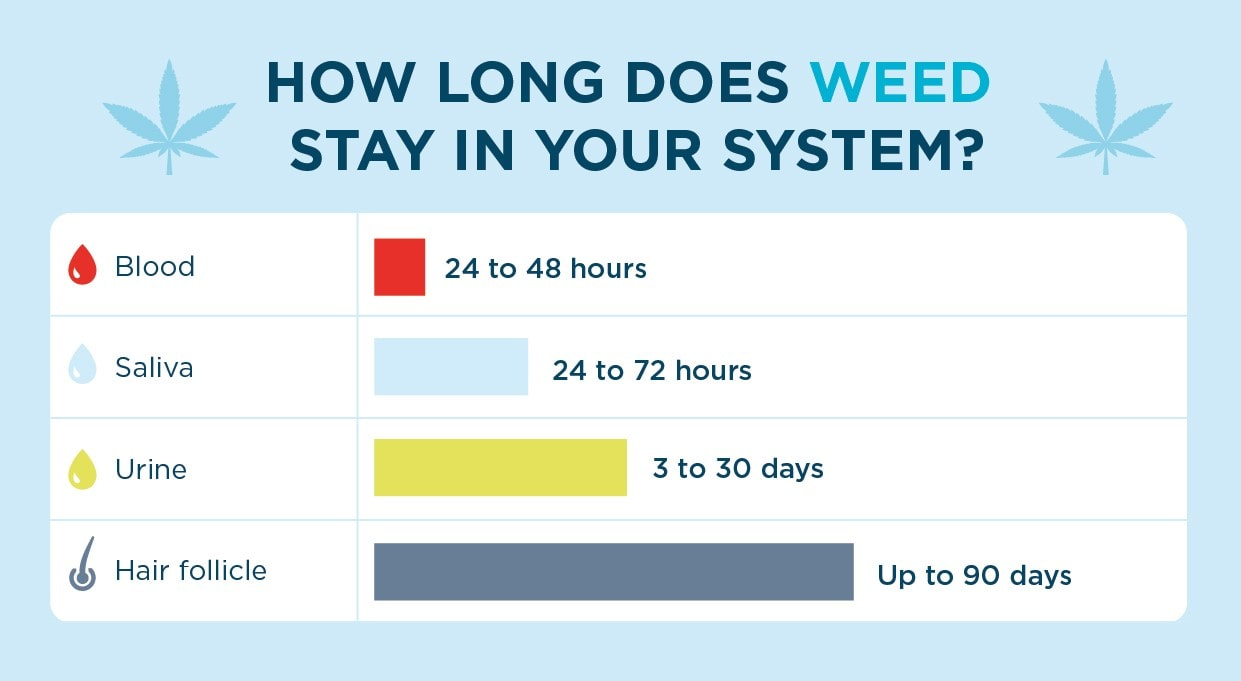
- Urine Test: THC metabolites can be detected for 3 to 30 days after last use, with heavy users potentially testing positive for up to 90 days.
- Blood Test: Detects active THC for 12 hours to 2 days, though chronic users may test positive for up to 30 days.
- Saliva Test: Detects THC for 24 to 72 hours after last use, depending on frequency.
- Hair Test: Can show THC presence for up to 90 days due to THC metabolites being incorporated into hair follicles.
Factors That Influence How Long Weed Stays in Your System
Several variables affect how long THC remains in the body:
- Frequency of Use: The more often cannabis is used, the longer it takes to clear from the system.
- Body Fat Percentage: Since THC is stored in fat cells, individuals with higher body fat tend to retain THC longer.
- Metabolism Rate: A faster metabolism will eliminate THC more quickly.
- Hydration Levels: Dehydration can lead to higher THC concentrations in urine, increasing detection times.
- Potency of Weed: High-THC strains stay in the system longer than low-THC varieties.
- Consumption Method: Edibles take longer to metabolize than smoked cannabis.
- Age & Overall Health: Older individuals and those with slower metabolisms may process THC more slowly.
Can You Cheat a Drug Test?
Many products claim to help users pass a urine test by diluting or masking THC, but most are unreliable. Employers and testing facilities often test for dilution and adulterants, making it difficult to game the system. The detection window varies based on multiple factors, including frequency of use, body fat percentage, metabolism, hydration levels, and the type of test used.
The length of time marijuana stays in the body depends on:
✔ How often you use it
✔ Your metabolism and body fat percentage
✔ The type of test being used
General THC Detection Windows
Below you can see how long weed stay in urine and can be detected.
| Test Type | Occasional Use | Regular Use | Chronic Heavy Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urine Test | 3-7 days | 7-15 days | 30+ days |
| Blood Test | 6-12 hours | 24-48 hours | Up to 7 days |
| Saliva Test | 24-48 hours | 48-72 hours | Up to a week |
| Hair Test | 30-90 days | 30-90 days | 90+ days |
These are estimates, as individual factors like metabolism, hydration, and BMI can affect the speed of THC elimination.
How Long Does THC Stay in Your Body for Testing?
How Long Does Weed Stay in Urine?
Urine tests are the most common drug screening method. Detection times depend on usage frequency:
- One-time use: 1-3 days
- Moderate use (3-4 times a week): 5-7 days
- Daily use: 10-15 days
- Heavy chronic use (multiple times daily): 30+ days
The half-life of THC in urine varies, meaning metabolites may be detected for longer in chronic users.
How Long Does THC Stay in Blood?
Blood tests primarily detect recent cannabis use:
- Casual users: Detectable for 12 hours to 2 days
- Heavy users: Can show THC for up to 30 days
Due to its short detection window, blood testing is rare outside of accident investigations or DUI assessments.
How Long Does THC Stay in Hair?
Hair follicle tests can detect weed in your system for up to 90 days. These tests do not measure current impairment but rather long-term cannabis use. Hair tests are less commonly used but are a concern for workplace screenings.
How Long Does Weed Stay in Saliva?
Saliva tests detect THC for:
- Occasional users: 24-48 hours
- Frequent users: Up to 72 hours
These tests are often used in roadside DUI checks because they can detect recent marijuana use.
How to Get Weed Out of Your System Faster
While there is no foolproof way to eliminate THC overnight, certain methods may help speed up the process:
- Increase Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush metabolites faster.
- Exercise Regularly: Cardio workouts help burn fat, where THC is stored.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Fiber-rich foods promote digestion and excretion of THC.
- Detox Drinks: Some claim to help cleanse the system, though effectiveness varies.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol slows metabolism, prolonging THC retention.
How Long Does Weed Stay In System After Quitting?
The same dose of cannabis can leave one person’s system in days while lingering for weeks in another. Here’s what affects THC retention:
1. Frequency of Use
- One-time users eliminate THC quickly.
- Daily users accumulate THC in fat, leading to longer detection times.
2. Body Fat Percentage
- Higher body fat = slower THC elimination since THC is stored in fat cells.
- People with lower BMI and fast metabolisms clear THC faster.
3. Metabolism & Hydration
- Faster metabolism = shorter THC retention.
- Hydration can dilute urine but doesn’t eliminate THC faster.
4. Consumption Method
- Smoking/vaping leads to faster absorption and elimination.
- Edibles take longer to process, staying in the body longer.
Can You Speed Up THC Elimination?
There’s no guaranteed way to instantly remove THC from your system, but some factors may help speed up the process.
✔ Hydration – Drinking water can dilute urine, but excessive hydration can cause a “diluted” test result, which may lead to a retest.
✔ Exercise – Boosts metabolism but may temporarily increase THC levels in blood as fat cells release stored THC.
✔ Healthy diet – Fiber-rich foods help excrete THC in feces, which is a primary elimination route.
✔ Time – The only foolproof way to pass a test is to let THC metabolize naturally.
What Doesn’t Work:
❌ Detox drinks & teas – Many mask urine dilution, but lab tests can detect them.
❌ Saunas & sweating – THC isn’t excreted through sweat.
❌ Vinegar, cranberry juice, or niacin – No scientific evidence supports these methods.
Secondhand Smoke & False Positives: Should You Worry?
- Casual exposure to secondhand smoke won’t trigger a positive test unless in an enclosed, unventilated space for an extended period.
- Saliva tests are most sensitive to secondhand exposure, but urine and blood tests are not.
Workplace & Legal Considerations
Even in states where cannabis is legal, many employers still test for THC.
- Some states (Nevada, New York) have banned pre-employment marijuana testing.
- Medical marijuana patients may still test positive, even with a prescription.
If you’re subject to workplace drug testing, always check your employer’s policies and state laws.

Key Takeaways
- Urine tests detect THC the longest (up to 30+ days for chronic users).
- Saliva tests detect recent use, up to 72 hours for most.
- Blood tests only detect active THC (up to 48 hours for occasional users).
- Hair tests provide a 90-day history but are not reliable for detecting recent use.
- Body fat, metabolism, and frequency of use all influence how long THC stays in the body.
If you are facing a drug test, the only way to be certain of passing is to allow THC to naturally metabolize over time.
If you’re concerned about drug tests, the best approach is to be informed, understand the variables, and avoid last-minute detox gimmicks.



